10 top biotechnology innovations 2023
To uncover the top biotechnology innovations set to have the biggest impact across science, medicine, engineering, and agriculture, we’ve analysed the data from our academia-industry matchmaking platform, Connect, to find the most promising technical innovations in development at universities around the world that the R&D community are most interested in.
The biotech innovations included in this year’s list are those that received the highest levels of engagement in 2022 from R&D professionals at companies including Johnson & Johnson, Roche, GSK, Syngenta, and Bayer using our platform to find new academic partners. The ranking factors in three metrics: 1) the number of introduction requests to the academic teams behind each project, 2) positive feedback from the companies reviewing them, and 3) total article reads.
Each of the features in our top biotechnology innovations list has been published on our online matchmaking platform, Connect, by a technology transfer office in a university or academic institute to find innovation-driven companies to collaborate with on further development, commercialisation and deployment.
A full non-confidential summary of each biotech innovation can be viewed on Connect through the links below each summary. Access to the platform is completely free for companies and there are no downstream fees associated with using it to connect with any of the 8,000 innovations showcased by the 250+ academic institutes subscribed. Create a free account here and get started connecting with unsurfaced research from universities and institutes worldwide.
Top Biotechnology Innovations
10. Genetically engineered plants to resist environmental stresses
9. Cell-free protein production platform
8. Reproductive Hormone from Cows, for Cows
7. New Strain of E. Coli for the Synthesis of Superior PHA
6. Broad Range Biodegradable Biosurfactants.
5. New Methods for Controlling Gene Expression in Agricultural Biotechnology
4. Recycling plastics with synthetic organisms
3. Genetically modified fibre crops to make waterproof materials
2. Universal Plant Gene Modification for More Efficient Growth
1. Naturally Occurring, Biocompatible Proteins for Tunable Proton Conduction
We’ve turned this list into a video if you would prefer to watch or listen through our top biotechnology innovations list. You can use the timestamps to navigate through the video to find those you’re most interested in, but to start a conversation with the team behind the project you will need to request an introduction through our platform.
10. Genetically Engineered Plants that Resist Environmental Stresses
Plant root epidermis have long root hair projections to increase their surface area for water and nutrient absorption. Phosphates are a key nutrient for plant growth and photosynthesis. However, the low concentration of phosphates in soil makes uptake difficult and can cause nutrient stress in plants.
Biotechnology researchers at the University of Pennsylvania have discovered that the overexpression of a gene, GRP8, increases the production of root hairs and thus, increased the surface area for water and nutrient absorption. The overexpression of this glycine-rich RNA-binding protein has also been found to improve plant tolerance to phosphate starvation, enhancing resistance to environmental stresses and reducing the need for fertiliser.
Read the full project summary to learn more about this top biotechnology innovations feature.
9. A Cell-free Protein Production Platform
Cell-free protein synthesis (CFPS) results in the production of proteins using biological transcription and translation processes without the need for living cells. Instead, this method uses a lysate containing all the essential macromolecules that facilitate the biological synthesis, however, lysate preparation is time-consuming and expensive, and so there is need for improved methods of CFPS.
Researchers at the Australian National University have developed a novel method for producing encapsulated cell-like structures (eCells) based on the lysate of E. coli for use in CFPS. This biotech breakthrough allows the efficient and cost-effective production of eCells, which in turn can be used to synthesise bioproducts of high commercial value and industrial relevance.
Read the full project summary to learn more about this top biotechnology innovations feature.
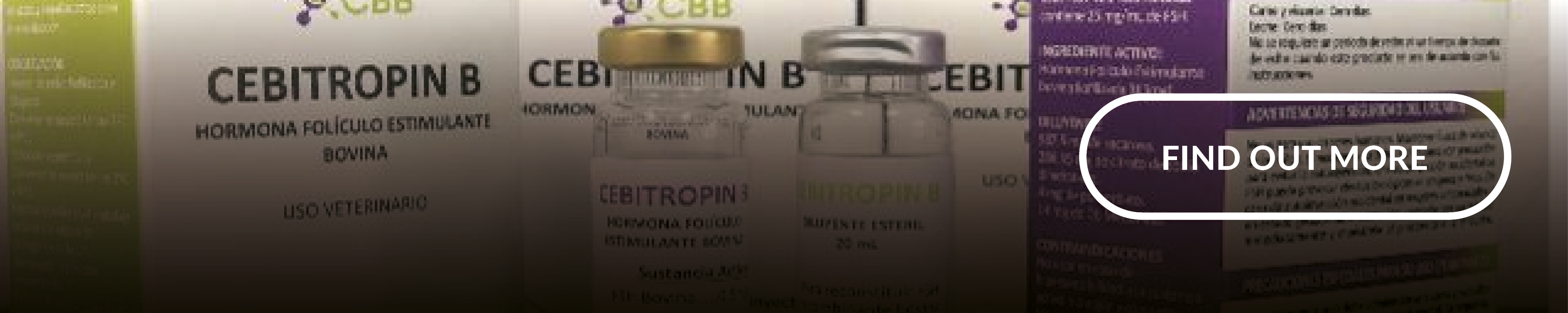
8. Reproductive Hormone from Cows, for Cows
Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) is widely used to assist reproduction in cattle breeding. However, the majority of FSH produced by biotechnology companies is sourced from pigs. This comes with significant risks when deployed in cattle, particularly with disease transmission between animal species and stimulating undesired immune responses.
To combat the dangers of using of porcine-derived FSH in cattle, a team of biotechnologists in South America represented Hub APTA have created a recombinant FSH from bovines, which successfully increases ovulation in cows with reduced risks, extended biological action time, and improved stability in the blood.
Read the full project summary to learn more about this top biotechnology innovations feature.
7. A New Strain of E. Coli for the Synthesis of Superior Biodegradable Plastics
As global plastic waste has more than doubled in the last 20 years, biodegradable plastics are becoming increasingly sought after. One class of promising biodegradable plastics are polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs), which are produced by the biotechnology industry through microbial fermentation.
With these PHA monomers being produced by microbes, their final composition can be difficult to control in a uniform way which affects the overall physical properties of the material. Now, however, State University of New York scientists have developed a new strain of E. coli that synthesises PHA copolymers with tailorable combinations of monomers, therefore allowing the physical properties to be adjusted and fine-tuned for each application.
Read the full project summary to learn more about this top biotechnology innovations feature.
6. Broad Range Biodegradable Biosurfactants
The use of surfactants in industries such as pharmaceuticals, food and biomedicine has become widespread due to their versatility in a range of applications including emulsifying, detergency and foaming. This versatility has seen surfactants become one of the most used process chemicals known to date. However, synthetically-made surfactants pose an increased environmental risk due to their difficulty in being degraded, leading to the requirement of more environmentally friendly bio-based surfactants.
A research team at the University of Western Cape have sought to tackle these environmental issues by developing alternative biotech solutions in the form of two patented compounds as part of a wider portfolio. These compounds showcase performance equivalent to industrial synthetic alternatives whilst also being biodegradable. This advancement within the biotech space will provide more sustainable and environmentally safer alternatives to synthetic surfactants whilst opening the door to screening for even more alternatives.
Read the full project summary to learn more about this top biotechnology innovations feature.
5. New Methods for Controlling Gene Expression in Agricultural Biotechnology
Growing populations and ever-changing global climates have opened the door to a myriad of challenges that affect food sources on a global scale. As such, the biotechnology industry has expedited a need to generate faster and more precise technologies in order to really push and create positive impacts on global food sources. One such constraint to this development of new food sources is the routine implementation of endogenous promoters during plant gene expression, the use of which makes controlling and fine-tuning said gene expression more difficult, and therefore delaying and even halting the production of new and improved plant species that can be used as food sources.
A research team at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory have devised a novel tri-pointed synthetic production strategy for transcription regulators by utilising key elements of yeast and plant species. The use of these elements allows the process to cover a diverse library of transcriptional regulators to control eukaryotic transcription. This technology will provide the agri-tech industry with an efficient way of coordinating the expression of multiple genes in a targeted, environmentally responsive and tissue-specific manner, giving way to the development of new and accessible food products on a global scale.
Read the full project summary to learn more about this top biotechnology innovations feature.
4. Recycling Plastics with Synthetic Organisms
The environmental impact of plastic is well known. But even so, only a small portion of it is still actually recycled. Consequently, this remains a pressing challenge for the biotechnology sector to address. Specifically, Polyethylene (PE), which makes up approximately 40% of all plastic production, including all petroleum-based polymers, is less than 20% is recycled.
Macquarie University researchers have developed a novel method that uses engineered microbial synthesis to produce moth, fungal and/or bacteria PE degrading enzymes. The result is the degradation or recycling of PE into commercially viable products (such as biofuels, fertilisers or other chemical products), creating an alternative to a major component of environmental plastic waste.
Read the full project summary to learn more about this top biotechnology innovations feature.
3. Genetically Modified Fibre Crops to make Waterproof Materials
As we move to find more sustainable materials for our everyday items, plants are increasingly seen as an environmentally-friendly route to the creation of biopolymers. Unfortunately, plant bast fibres, a major source of these biopolymers, present a drawback that affects the mechanical properties of the material; the absorption of moisture.
Biotech researchers at the Luxembourg Institute of Science and Technology have developed an alternative method to create fibre crops that express amphipathic proteins which can form monolayers at hydrophilic-hydrophobic interfaces. These could work as a suitable substitute to widely-used chemical methods used to achieve permeability, as this method doesn’t cause negative changes in the bast fibres morphology.
Read the full project summary to learn more about this top biotechnology innovations feature.
2. Universal Plant Gene Modification for More Efficient Growth
Human population growth and climate change are placing increasing pressure on the production of crops with improved nitrogen use efficiency, for nutrition in agriculture and environmental carbon sequestration. The expression and importance of early nodulin (ENOD) genes have been shown to be essential for nitrogen-fixing nodule formation and have been applied to increase nitrogen use efficiency. However, because researchers haven’t fully understood how ENOD works to alter plant growth, characteristics and development, it has not been used efficiently.
At the University of Western Australia, scientists have identified the role of ENOD93 gene inside plant cells, enabling targeted tuning and manipulation of ENOD93 in plants during specific phases of their lifecycle. This biotechnology will allow for the control over the development of desirable characteristics in plants (e.g. nitrogen use efficiency, rapid flowering, resilience, fertility, growth and biomass) to economically and sustainably meet growing demands for crop production.
Read the full project summary to learn more about this top biotechnology innovations feature.
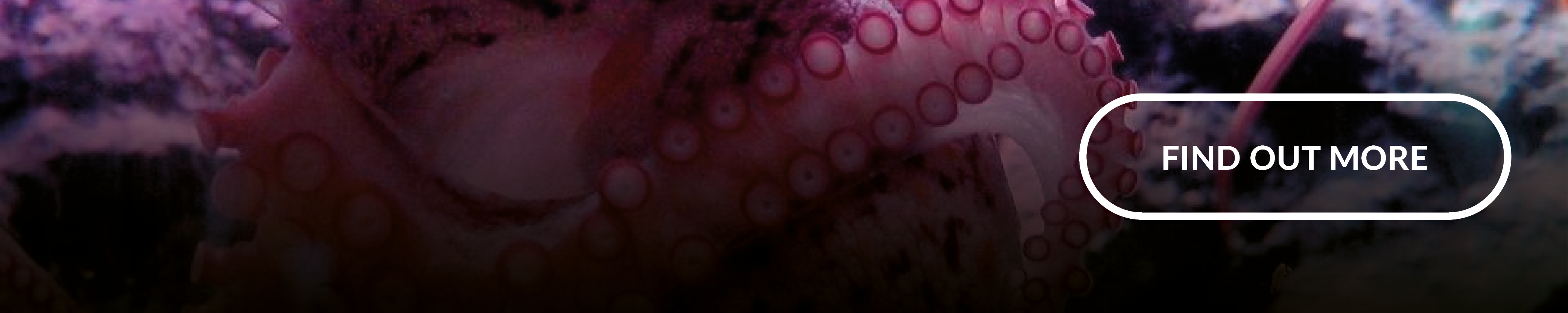
1. Naturally Occurring, Biocompatible Proteins for Tunable Proton Conduction
Proton-conducting materials are essential for renewable energy and bioelectronics technologies. Many modern devices rely on the transport of protons, ranging from fuel cells and transistors to biosensors and medical implants. Protein-based proton-conducting materials have received considerably less attention than other, man-made materials, despite offering greater potential for modularity, tunability and processability.
Researchers at the University of California, Irvine have fabricated a biocompatible and versatile proton-conducting material from naturally occurring, structural proteins found in cephalopods. These Proton-Conducting Cephalopod Proteins (“PCCPs”) can withstand heat and acidity and can be modified using genetic engineering techniques to tune the resulting electrical properties to different specifications, allowing ease of integration into protonic flow systems.
Read the full project summary to learn more about this top biotechnology innovations feature.
What do we classify as a ‘biotechnology innovation’?
For this top biotechnolgy innovations list, a ‘biotechnology innovation’ is a technology that utilises biological systems, and living organisms to develop or create different products. Examples of processes that use biotechnology are brewing and baking bread, as they both use yeast, a living organism to create a product.
Applications of biotechnology include therapeutics and diagnostics for a range of diseases, bioremediation, waste treatment, sustainable energy production and genetically modified crops for improving agriculture and food production.
A (very) brief history of biotechnology
One of the earliest examples of biotechnology is in the selective breeding of crops to increase beneficial characteristics such as yields, nutritional value, disease-, drought-, and pest resistance. Traditional plant breeding methods have created seedless watermelons, grape tomatoes, and broccolini.
Biotechnology arose from the German field of zymotechnology, which began as a search for a better understanding of industrial fermentation from known fermentation processes in the production of food and drinks. The zymotechnology industry boomed during World War I with the increased demand for products such as animal feed and lactic acid, a replacement for hydraulic fluid.
The Hungarian Károly Ereky coined the word biotechnology in Hungary in 1919 to describe a technology that converted raw materials into a more useful product. Other milestones in biotechnology history include the mass production of penicillin in the 1940s using a fermentation process developed in America.
From 1945 onwards, the field of biotechnology has focused on harnessing genetic engineering and creating new medicines like vaccines and mass-producing others, like insulin. In 1994, genetically modified crops were first introduced in the USA. There are currently 13 crops with GM varieties commercially available around the world.
The biotechnology industry has shown rapid growth since the 1970s and the global biotechnology market is currently valued at 752.8 Billion. Biotech companies globally have reached a combined value of $2.0 trillion.
What does the future hold for biotechnology innovations?
There are many challenges that the biotechnology industry face. There is a high level of risk involved in developing biotechnology innovations and the associated trials and ensuring the costs are covered through patents and licensing deals. There are many ethical considerations involved in biotechnology as the use of genetics increases, from how to protect patient privacy to social concerns, such as the controversy surrounding GM crops and GMOs.
Despite these challenges, the development of breakthrough health initiatives from biotechnology innovations will transform our future as we tackle global challenges including health, medicine, and agriculture. Labiotech recently interviewed Bill Coyle, principal, ZS on their prediction for the trends and priorities in biotechnology in 2023. Bill cited cancer, antimicrobial resistance, and sepsis as the areas with the most potential for development in 2023, but also mentioned applications of biotech in a range of non-life science research areas including climate change and food security.
Skip to top
Written by: Frances Wilkinson, Jolie Hamilton-Warford (1, 2), Mireia Baizan-Urgell (3, 4), Nathan Ford (5, 6), Daisy (7, 8), Ella Cliff, (9, 10). Edited by Frances Wilkinson and Jake Mitchell.
Copyrights reserved unless otherwise agreed – IN-PART Publishing Ltd., 2023: ‘Top biotechnology innovations’
What is IN-PART?
IN-PART develops digital solutions, curated by in-house STEM experts, that simplify the initial connection between decision-makers in academia and industry. Our goal is to help drive impact from research by matching innovation and expertise on a level playing field globally.
Connect, a digital partnering platform for university-industry collaboration.
An online matchmaking platform used by 250+ universities and research institutes to connect with industry teams in 6,000+ companies to commercialise academic innovations and expertise that are available and seeking collaboration.
Discover, a bespoke scouting service for open innovation.
A bespoke scouting platform used by innovation-driven companies to profile the global landscape of academia across an active network of 2,600+ institutes, either through ‘Industry Calls for Opportunities’ or ‘Request for Proposal’ campaigns that find and confirm potential solutions to specific R&D challenges or requirements.

Header image credit: motorolka/ AdobeStock
In-line image credit (in order of appearance): IRRI Images / Wikimedia, CC BY 2.0, J. N. Eskra / Wikimedia Commons, CC BY-SA 4.0, APTA, Arsenii / stock.adobe.com, rh2010 / stock.adobe.com, Couleur / pixabay license, RHJ / stock.adobe.com, Robert Knapp / stock.adobe.com, lovelyday12 / stock.adobe.com, bearinthenorth / Pixabay, CC0.